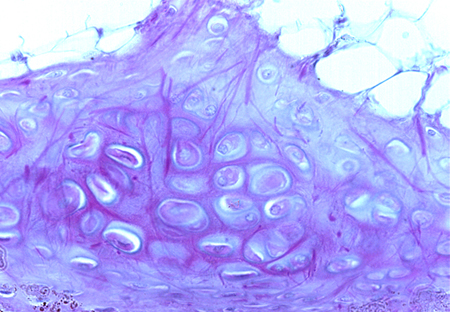
ELASTIC CARTILAGE
The most important feature of an elastic cartilage is the composition of its extracellular matrix. It contains a large amount of elastic material, primarily in the form of elastic fibers, as well as varying amounts of collagen.
This peculiarity gives elastic cartilage pieces greater elasticity than that found in hyaline cartilage pieces. It is found, for example, in the larynx, epiglottis, and ear.
Its appearance in hematoxylin and eosin-stained sections can be very similar to that of hyaline cartilage. The elastic fibers are not usually stained with this combination of dyes. To properly diagnose elastic cartilage, it is very useful to use dyes that demonstrate elastic material (e.g., Verhoeff’s stain, Weigert’s stain).
This peculiarity gives elastic cartilage pieces greater elasticity than that found in hyaline cartilage pieces. It is found, for example, in the larynx, epiglottis, and ear.
Its appearance in hematoxylin and eosin-stained sections can be very similar to that of hyaline cartilage. The elastic fibers are not usually stained with this combination of dyes. To properly diagnose elastic cartilage, it is very useful to use dyes that demonstrate elastic material (e.g., Verhoeff’s stain, Weigert’s stain).
In both images, observe a elastic fibers in the cartilage extracellular matrix, as well as chondrocytes (several are highlighted in the upper image when you move the cursor over it).
External ear. Staining: Weigert. Magnification: medium.


Trachea. Staining: Weigert. Magnification: medium.